Netty 之轮盘定时器 HashedWheelTimer
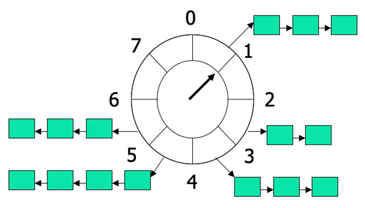
轮盘定时器原理概述
轮盘定时器用来实现任务的延期执行。
tick,节拍,每过一个节拍,指针移动一个刻度ticksPerWheel,轮盘一圈包含的节拍数,也就是轮盘总刻度数tickDuration,节拍间距,也就是指针走完相邻刻度的时长roundDuration,计时周期,轮盘指针走完一圈耗时,。当任务的延期时长delay超出计时周期时,任务放入对应桶中的同时保存剩余圈数:- 桶,相邻刻度之间为桶,桶中以链表或其他形式存放延时任务。当指针走过该桶时,桶中超时的延时任务开始启动
HashedWheelTimeout
延时任务句柄,当用户向定时器提交延时任务时,定时器返回一个延时任务句柄。通过延时句柄,用户可以查看延时任务状态,取消延时任务,获取延时任务等。定时器内部,也是在桶的双链表中以延时任务句柄的形式存放延时任务及其他相关信息。
#cancel
修改延时任务状态为ST_CANCELLED,修改失败,返回 FALSE。
如果状态修改成功,则把延时任务加入任务取消队列cancelledTimeouts,返回 TRUE。在下一个节拍到来时,定时器会把取消队列cancelledTimeouts中所有的延时任务句柄从轮盘桶中移除,见#run和#processCancelledTasks。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public boolean cancel() {
// 修改句柄状态为 ST_CANCELLED
if (!compareAndSetState(ST_INIT, ST_CANCELLED)) {
// 修改失败返回 FALSE
return false;
}
// 仅仅把任务句柄放入取消队列 cancelledTimeouts,
// 最多一个节拍的时间之后,我们会把它从桶中移除
timer.cancelledTimeouts.add(this);
// 取消成功
return true;
}
#expire
修改延时任务句柄状态为ST_EXPIRED,修改成则运行延时任务,否则直接返回。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public void expire() {
// 修改任务句柄状态为 ST_EXPIRED
if (!compareAndSetState(ST_INIT, ST_EXPIRED)) {
// 修改失败直接返回
return;
}
try {
// 修改成功,运行延时任务
task.run(this);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("An exception was thrown by "
+ TimerTask.class.getSimpleName() + '.', t);
}
}
}
#remove
从对应轮盘桶中删除本延时任务句柄。该方法会在#processCancelledTasks中调用。延时任务句柄先被取消,然后才会被移除。如果延时任务句柄还没有加入到某个轮盘桶中,也就是还在队列timeouts中,那么只需要递减等待任务数就好,在下一个节拍到来时,定时器会把它从队列timeouts中移除。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
void remove() {
HashedWheelBucket bucket = this.bucket;
if (bucket != null) {
// 已经在桶中,直接移除
bucket.remove(this);
} else {
// 还没有加入轮盘桶,还在队列 timeouts 中,直接递减等待任务数
timer.pendingTimeouts.decrementAndGet();
}
}
HashedWheelTimer
时间计算问题没有搞清楚
构造函数
内部以循环数组来保存所有的轮盘桶,桶内以链表结构存放延时任务句柄。当轮盘指针指向某刻度时,检查该刻度对应的桶内任务是否超时(到达执行时间)。
maxPendingTimeouts为定时器中最大延时任务句柄数。
HashedWheelTimer实例比较消耗 CPU,因此同一个 JVM 中不应该创建多于 1 个实例。默认第一次创建的实例数超过 64 时,会输出日志告警。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
public HashedWheelTimer(
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
long tickDuration, TimeUnit unit, int ticksPerWheel, boolean leakDetection,
long maxPendingTimeouts) {
// 此处忽略部分字段校验
// 创建轮盘,节拍数为大于等于 ticksPerWheel 的 2 的 N 次幂
wheel = createWheel(ticksPerWheel);
// 循环数组掩码
mask = wheel.length - 1;
// 初始化节拍间隔,单位『纳秒』
this.tickDuration = unit.toNanos(tickDuration);
// 防止溢出
if (this.tickDuration >= Long.MAX_VALUE / wheel.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"tickDuration: %d (expected: 0 < tickDuration in nanos < %d",
tickDuration, Long.MAX_VALUE / wheel.length));
}
// 初始化『苦工线程』
workerThread = threadFactory.newThread(worker);
// 是否开启内存泄露检测
leak = leakDetection || !workerThread.isDaemon() ? leakDetector.track(this) : null;
// 最大等待任务数
this.maxPendingTimeouts = maxPendingTimeouts;
// HashedWheelTimer 实例数第一次超出 64 告警
if (INSTANCE_COUNTER.incrementAndGet() > INSTANCE_COUNT_LIMIT &&
WARNED_TOO_MANY_INSTANCES.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
reportTooManyInstances();
}
}
// 创建轮盘,初始化轮盘桶,一个节拍一个桶
private static HashedWheelBucket[] createWheel(int ticksPerWheel) {
if (ticksPerWheel <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"ticksPerWheel must be greater than 0: " + ticksPerWheel);
}
if (ticksPerWheel > 1073741824) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"ticksPerWheel may not be greater than 2^30: " + ticksPerWheel);
}
// 规范化为 2 的 N 次幂
ticksPerWheel = normalizeTicksPerWheel(ticksPerWheel);
HashedWheelBucket[] wheel = new HashedWheelBucket[ticksPerWheel];
for (int i = 0; i < wheel.length; i ++) {
// 初始化节拍桶,一个节拍一个桶
wheel[i] = new HashedWheelBucket();
}
return wheel;
}
// 大于等于 ticksPerWheel 且最小的 2 的 N 次幂
private static int normalizeTicksPerWheel(int ticksPerWheel) {
int normalizedTicksPerWheel = 1;
while (normalizedTicksPerWheel < ticksPerWheel) {
normalizedTicksPerWheel <<= 1;
}
return normalizedTicksPerWheel;
}
#newTimeout
添加延时任务task到轮盘定时器,delay为延迟执行时间,返回延时句柄。此时,延时句柄还没有被添加到轮盘某桶的链表中,也就延时任务还没有启动计时,在下一个节拍到来时才会被加入轮盘桶中,启动计时。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
public Timeout newTimeout(TimerTask task, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
if (unit == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("unit");
}
// 等待任务数自增 1
long pendingTimeoutsCount = pendingTimeouts.incrementAndGet();
// 等待任务数超标检测
if (maxPendingTimeouts > 0 && pendingTimeoutsCount > maxPendingTimeouts) {
pendingTimeouts.decrementAndGet();
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Number of pending timeouts ("
+ pendingTimeoutsCount + ") is greater than or equal to "
+ "maximum allowed pending timeouts (" + maxPendingTimeouts + ")");
}
// 视定时器状态,启动『苦工线程』
start();
// 延时任务执行时间
long deadline = System.nanoTime() + unit.toNanos(delay) - startTime;
// 创建延时句柄
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = new HashedWheelTimeout(this, task, deadline);
// 添加延时句柄到队列 timeouts
timeouts.add(timeout);
// 返回
return timeout;
}
// 视定时器状态,启动『苦工线程』
public void start() {
// 定时器状态为 WORKER_STATE_INIT 时,启动『苦工线程』
// 并置定时器状态为 WORKER_STATE_STARTED
// 其他状态非法
switch (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.get(this)) {
case WORKER_STATE_INIT:
if (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(
this, WORKER_STATE_INIT, WORKER_STATE_STARTED)) {
workerThread.start();
}
break;
case WORKER_STATE_STARTED:
break;
case WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN:
throw new IllegalStateException("cannot be started once stopped");
default:
throw new Error("Invalid WorkerState");
}
// 等待『苦工线程』初始化定时器启动时间
while (startTime == 0) {
try {
startTimeInitialized.await();
} catch (InterruptedException ignore) {
// Ignore - it will be ready very soon.
}
}
}
#stop
关闭轮盘定时器。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
public Set<Timeout> stop() {
if (Thread.currentThread() == workerThread) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
HashedWheelTimer.class.getSimpleName() +
".stop() cannot be called from " +
TimerTask.class.getSimpleName());
}
if (!WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this,
WORKER_STATE_STARTED, WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN)) {
// workerState can be 0 or 2 at this moment - let it always be 2.
if (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.getAndSet(this, WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN)
!= WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN) {
INSTANCE_COUNTER.decrementAndGet();
if (leak != null) {
boolean closed = leak.close(this);
assert closed;
}
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
while (workerThread.isAlive()) {
workerThread.interrupt();
try {
workerThread.join(100);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
interrupted = true;
}
}
if (interrupted) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
} finally {
INSTANCE_COUNTER.decrementAndGet();
if (leak != null) {
boolean closed = leak.close(this);
assert closed;
}
}
return worker.unprocessedTimeouts();
}
HashedWheelBucket
定时器中的延时任务实际都存放在轮盘桶中。桶内部为双链表结构。
#addTimeout
向当前桶中添加一个延时任务句柄。也就是向桶内的双链表插入任务句柄。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public void addTimeout(HashedWheelTimeout timeout) {
// 确保任务句柄没有被加过轮盘桶
assert timeout.bucket == null;
// 设置句柄所属的桶
timeout.bucket = this;
// 句柄加入双向链表
if (head == null) {
head = tail = timeout;
} else {
tail.next = timeout;
timeout.prev = tail;
tail = timeout;
}
}
#expireTimeouts
过期桶中的任务句柄。
当轮盘指针走过当前桶时,桶中部分任务句柄中的任务延迟时间已到,启动任务执行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
public void expireTimeouts(long deadline) {
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = head;
// 从表头开始,依次检查任务句柄
while (timeout != null) {
HashedWheelTimeout next = timeout.next;
// 等待圈数已归 0,说明当前任务已过期,可以执行了
if (timeout.remainingRounds <= 0) {
// 从链表中删除该任务句柄,并获取下一个任务句柄
next = remove(timeout);
// 检查是否到延迟执行时间点,理论上都是 ok 的
if (timeout.deadline <= deadline) {
// 执行延时任务
timeout.expire();
} else {
// 理论上永不发生,能被雷劈?
throw new IllegalStateException(
String.format(
"timeout.deadline (%d) > deadline (%d)",
timeout.deadline,
deadline
)
);
}
}
// 圈数未归 0,检查是否被取消
else if (timeout.isCancelled()) {
// 当前句柄被取消,删除并获取下一个任务句柄
next = remove(timeout);
}
// 圈数未归 0,圈数递减 1
else {
timeout.remainingRounds --;
}
// 检查下一个
timeout = next;
}
}
#remove
在延时任务被执行或者被取消时,调用#remove方法,从链表中删除该延时任务句柄节点,并递减定时器等待任务数,最终返回它的后驱节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
public HashedWheelTimeout remove(HashedWheelTimeout timeout) {
HashedWheelTimeout next = timeout.next;
if (timeout.prev != null) {
// 有前驱
timeout.prev.next = next;
}
if (timeout.next != null) {
// 有后驱
timeout.next.prev = timeout.prev;
}
if (timeout == head) {
// timeout 是表头指针
if (timeout == tail) {
tail = null;
head = null;
} else {
head = next;
}
} else if (timeout == tail) {
// timeout 是表尾指针
tail = timeout.prev;
}
// 置 null,方便 GC.
timeout.prev = null;
timeout.next = null;
timeout.bucket = null;
// 递减定时器等待任务数
timeout.timer.pendingTimeouts.decrementAndGet();
// 返回后驱节点
return next;
}
#pollTimeout
拿出并删除链表中的表头节点代表的延时任务句柄,没有返回null。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
private HashedWheelTimeout pollTimeout() {
HashedWheelTimeout head = this.head;
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
HashedWheelTimeout next = head.next;
if (next == null) {
tail = this.head = null;
} else {
this.head = next;
next.prev = null;
}
// null out prev and next to allow for GC.
head.next = null;
head.prev = null;
head.bucket = null;
return head;
}
#clearTimeouts
把桶中的延时任务句柄从链表结构中转移到传入参数集合set中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public void clearTimeouts(Set<Timeout> set) {
for (;;) {
// 拿出表头
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = pollTimeout();
if (timeout == null) {
return;
}
if (timeout.isExpired() || timeout.isCancelled()) {
// 忽略已过期(执行)、已取消句柄
continue;
}
// 加入集合
set.add(timeout);
}
}
Worker
轮盘定时器的定时功能由苦工Worker提供。Worker实现了Runnable接口。
#run
#run方法内部实现了定时器的主要工作流程。
- 等待节拍的到来(指针移动);
- 移除被取消的任务句柄;
- 把队列
timeouts中没有被取消的任务句柄转移到对应的桶中; - 执行当前指针走过的桶中已到期的任务;
- 节拍递增 1(指针到达下一刻度);
- 从头再来一遍,直到定时器被关闭。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
public void run() {
// 初始化定时器启动时间
startTime = System.nanoTime();
if (startTime == 0) {
// 未初始化的启动时间为 0
// 为了区别,如果#nanoTime 刚好返回了 0 值,我们设置启动事件为 1
startTime = 1;
}
// 通知阻塞在 HashedWheelTimer#start的线程结束等待
startTimeInitialized.countDown();
do {
// 定时器走一个节拍
final long deadline = waitForNextTick();
if (deadline > 0) { // 正常走完节拍
// 计算原先轮盘指针位置
int idx = (int) (tick & mask);
// 处理已取消任务
processCancelledTasks();
// 把任务句柄从队列 timeouts 中正式加入对应的桶中
transferTimeoutsToBuckets();
// 获取当前轮盘指针走过的桶
HashedWheelBucket bucket = wheel[idx];
// 执行桶中已到期的任务
bucket.expireTimeouts(deadline);
// 节拍数递增 1
tick++;
}
} while (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.get(HashedWheelTimer.this) == WORKER_STATE_STARTED);
// Fill the unprocessedTimeouts so we can return them from stop() method.
for (HashedWheelBucket bucket: wheel) {
bucket.clearTimeouts(unprocessedTimeouts);
}
for (;;) {
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = timeouts.poll();
if (timeout == null) {
break;
}
if (!timeout.isCancelled()) {
unprocessedTimeouts.add(timeout);
}
}
processCancelledTasks();
}
#waitForNextTick
定时器走一个节拍,轮盘指针移动一个刻度,并返回指针移动完成的时间点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
private long waitForNextTick() {
// 计算走一个节拍的完成时间点
long deadline = tickDuration * (tick + 1);
for (;;) {
// 定时器当前时间点
final long currentTime = System.nanoTime() - startTime;
// 计算走一个节拍的等待时间,即定时器休眠时间,取天花板
long sleepTimeMs = (deadline - currentTime + 999999) / 1000000;
// 睡眠结束,要么出错,要么正常
if (sleepTimeMs <= 0) {
if (currentTime == Long.MIN_VALUE) {
return -Long.MAX_VALUE;
} else {
// 睡眠结束,返回当前时间点
return currentTime;
}
}
// 早期部分 windows 系统的睡眠时间需要是 10ms 的整数倍
// 否则会有 bug
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/356
if (PlatformDependent.isWindows()) {
sleepTimeMs = sleepTimeMs / 10 * 10;
}
try {
// 睡吧,看能不能睡满 sleepTimeMs
Thread.sleep(sleepTimeMs);
}
// 休眠被中断
catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
// 如果定时器状态为关闭状态 WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN
if (WORKER_STATE_UPDATER.get(HashedWheelTimer.this) == WORKER_STATE_SHUTDOWN) {
// 返回 Long.MIN_VALUE
return Long.MIN_VALUE;
}
// 否则,下一轮我们继续睡
}
}
}
#processCancelledTasks
处理被取消任务。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
private void processCancelledTasks() {
for (;;) {
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = cancelledTimeouts.poll();
if (timeout == null) {
// all processed
break;
}
try {
timeout.remove();
} catch (Throwable t) {
// just log warn
}
}
}
#transferTimeoutsToBuckets
把没有被取消的延时任务句柄从队列timeout中转移到对应的轮盘桶中。为了防止用户没完没了的往定时器中提交延时任务,导致本方法不能及时返回而影响定时器的正常工作,每次调用,最多只会转移十万个任务句柄。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
private void transferTimeoutsToBuckets() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
HashedWheelTimeout timeout = timeouts.poll();
if (timeout == null) {
// 队列 timeouts 中没有句柄了
break;
}
if (timeout.state() == HashedWheelTimeout.ST_CANCELLED) {
// 句柄已被取消,忽略之
continue;
}
// 计算剩余圈数
long calculated = timeout.deadline / tickDuration;
timeout.remainingRounds = (calculated - tick) / wheel.length;
// 计算所属的桶
// Ensure we don't schedule for past.
final long ticks = Math.max(calculated, tick);
int stopIndex = (int) (ticks & mask);
// 加入对应的桶
HashedWheelBucket bucket = wheel[stopIndex];
bucket.addTimeout(timeout);
}
}
#unprocessedTimeouts
1
2
3
public Set<Timeout> unprocessedTimeouts() {
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(unprocessedTimeouts);
}



